
Project management is essential for any organization that wants to achieve its goals in a structured and efficient way. This guide breaks down the fundamentals, including what project management entails, its key components, the role of a project manager, and the common methodologies in use today.
1. WHAT IS PROJECT MANAGEMENT
Project management is the process of planning, executing, and overseeing projects to meet specific goals within a set timeline, scope, and budget. A project is a temporary endeavor, with a clear beginning and end, and aims to create a unique product, service, or result.
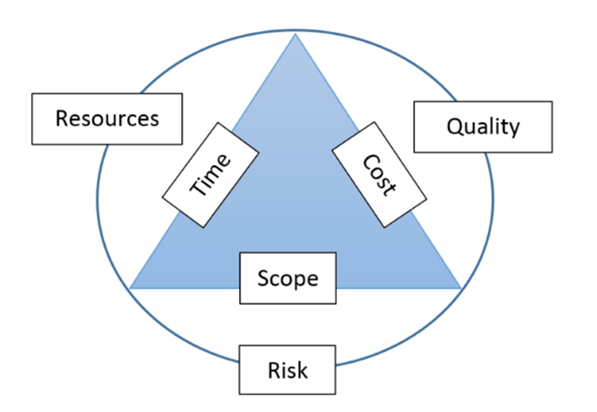
Key Constraints
- Scope
- Time
- Cost
- Quality
- Stakeholders
- Risks.
2. WHY IS PROJECT MANAGEMENT IMPORTANT
Project management is crucial because it ensures that projects are completed on time, within budget, and to the required specifications. It involves the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. Here are some key reasons why project management is important:
Effective project management ensures:
- Scope Management: Project scope management is a critical component of project management that ensures that a project is completed within its intended scope, budget, and timeline, and meets the expectations of its stakeholders.
- Timely Completion: Project management helps plan and schedule tasks effectively, ensuring that projects are completed within the set deadlines.
- Budget Management involves careful budgeting and cost management, which helps keep the project within financial constraints.
- Quality Assurance: Project management ensures the project meets the required quality standards and specifications.
- Resource Optimization: It helps in the efficient allocation and utilization of resources, including human resources, materials, and equipment.
- Risk Management: Project management involves identifying potential risks and developing strategies to mitigate them, ensuring smoother project execution.
Project management helps organizations avoid the pitfalls of poor planning, inadequate resource management, and miscommunication. Also, it helps organizations save time and money, improve quality, and enhance overall project performance. By using various tools and techniques, project managers can ensure that projects are delivered successfully, meeting the expectations of stakeholders.
3. THE ROLE OF A PROJECT MANAGER
The project manager is responsible for leading the team, coordinating tasks, and ensuring that project objectives are met. Key responsibilities include:
- Identifying Project Goals, Needs, and Scope: Defining the objectives, deliverables, and boundaries of the project to ensure clarity and alignment with stakeholders.
- Planning, Monitoring, and Documenting Tasks: Creating detailed project plans, schedules, and documentation to track progress and ensure that all tasks are completed as planned.
- Ensuring Timely Delivery: Managing all tasks, deliverables, and project materials to ensure they are delivered on time and meet the required quality standards.
- Resource Management: Allocating and managing all resources necessary for project execution, including human resources, materials, and equipment.
- Effective Communication: Fostering clear and consistent communication with stakeholders regarding project status, risks, and issues.
- Risk Management: Foreseeing potential blockers and developing strategies to mitigate or eliminate them to ensure project success.
A project manager is a key figure in ensuring the successful completion of a project. They coordinate all resources, plan and organize tasks, direct project activities, and control project execution to achieve the stated objectives. By effectively managing these responsibilities, project managers help organizations deliver projects that meet or exceed stakeholder expectations.
4. KEY PROJECT MANAGEMENT PHASES
Project management typically involves several key phases that guide a project from inception to completion. These phases ensure that the project is well-planned, executed efficiently, and completed successfully. The main phases of project management are:
- Initiation: This phase involves defining the project at a high level. Key activities include developing a project charter, identifying stakeholders, and setting initial project goals and objectives. The project charter is a critical document that formally authorizes the project and provides a clear direction.
- Planning: In this phase, detailed planning is conducted to outline how the project will be executed and controlled. This includes developing a project management plan, defining the project scope, creating a work breakdown structure (WBS), scheduling tasks, estimating costs, and planning for risk management. Project Plan/Project Definition
- Execution: This phase involves coordinating people and resources to carry out the project plan. Key activities include managing teams, executing tasks, ensuring quality, and communicating with stakeholders. The project manager plays a crucial role in directing and managing project work during this phase.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Throughout the project, monitoring and controlling processes are used to track progress, identify any variances from the plan, and implement corrective actions as needed. This phase ensures that the project stays on track concerning scope, time, cost, and quality.
- Closing: The final phase involves completing all project activities, obtaining formal acceptance of the project deliverables, and closing out the project. This includes finalizing all project documentation, releasing project resources, and conducting a post-project evaluation to capture lessons learned.
The key phases of project management provide a structured approach to managing projects from start to finish. By following these phases, project managers can ensure that projects are well-planned, executed efficiently, and completed successfully, ultimately delivering value to stakeholders.
5. POPULAR PROJECT MANAGEMENT METHODOLOGIES
Project management methodologies provide structured approaches to planning, executing, and completing projects. Different methodologies are suited to different types of projects and organizational needs. Here are some of the most popular project management methodologies:
- Waterfall (Prediction): A linear and sequential approach where each phase must be completed before the next one begins. It is best suited for projects with well-defined requirements and where changes are minimal.
- Agile (Scrum): An iterative and incremental approach that emphasizes flexibility and customer satisfaction. Agile methodologies, such as Scrum and Kanban, are ideal for projects where requirements are expected to evolve.
- Hybrid: Combines elements from different methodologies, such as Agile and Waterfall, to meet specific project needs.
- Lean: Focuses on maximizing value by eliminating waste and improving processes. Lean principles are often applied in manufacturing but can be adapted to other industries to enhance efficiency.
- PRINCE2 (Projects IN Controlled Environments): A process-based methodology that provides a detailed framework for managing projects. It is widely used in the UK and Europe and emphasizes business justification, defined roles, and a product-based planning approach.
Adhere the selecting the right project management methodology depends on the project’s nature, complexity, and specific requirements. Each methodology offers unique advantages and can be tailored to fit the needs of different projects and organizations. By understanding and applying these methodologies, project managers can improve project outcomes and achieve their goals more effectively.
6. PROJECT MANAGEMENT TOOLS AND SOFTWARE
Using the right tools is crucial for effective project management. Here are some common project management tools:
- Technical BIM Tools: Building Information Modeling (BIM) software is a powerful tool used in the construction and architecture industries to create and manage digital representations of the physical and functional characteristics of buildings. BIM software integrates various aspects of a project, including design, construction, operation, and maintenance, into a single, cohesive model.
- Scheduling Tools: Microsoft Project, Primavera P6, Excel, Visio, etc. These tools are extensively used for planning and scheduling project tasks. They help in creating project timelines, setting deadlines, and tracking progress. Popular scheduling tools include Gantt charts and network diagrams, which provide visual representations of project schedules.
- Risk Management Tools: Excel, Primavera Risk Analysis, etc. These tools help in identifying, analyzing, and managing project risks. They provide features for risk assessment, mitigation planning, and monitoring. By using risk management tools, project managers can proactively address potential issues and minimize their impact on the project.
- Reporting and Analytics Tools: Excel, Tower BI, etc. These tools generate reports and provide insights into project performance. They help in tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), analyzing project data, and making data-driven decisions. Examples include Microsoft Power BI and Tableau.
- Collaboration and Communication Tools: Email, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, etc. These tools effective communication is crucial for project success. Collaboration tools facilitate communication among team members and stakeholders, allowing for real-time updates, file sharing, and collaborative workspaces.
Project management tools and software are vital for ensuring the successful completion of projects. They provide the necessary functionalities to manage resources, budgets, schedules, risks, and communication effectively. By leveraging these tools, project managers can enhance project performance, improve efficiency, and achieve project goals.
7. COMMON CHALLENGES IN PROJECT MANAGEMENT AND HOW TO OVERCOME THEM
Project management often involves navigating a variety of challenges that can impact the successful delivery of a project. Understanding these common challenges and implementing strategies to overcome them is crucial for project managers. Here are some of the most common challenges in project management and ways to address them:
- Scope Creep: This occurs when the project scope expands beyond its original objectives, often due to uncontrolled changes or additional features.
- Solution: Implement a robust change management process, clearly define project scope, and ensure all changes are documented and approved by stakeholders.
- Lack of Clear Goals and Objectives: Projects can struggle without well-defined goals and objectives, leading to confusion and misalignment among team members.
- Solution: Develop a detailed project charter and scope statement, and ensure all stakeholders have a clear understanding of the project’s goals and objectives.
- Poor Communication: Ineffective communication can lead to misunderstandings, missed deadlines, and a lack of coordination among team members.
- Solution: Establish clear communication channels, hold regular meetings, and use collaboration tools to keep everyone informed and engaged.
- Resource Management Issues: Inefficient allocation and utilization of resources can lead to delays and increased costs.
- Solution: Use resource management software to track and allocate resources effectively, and ensure that resource planning is integrated into the project plan.
- Risk Management: Unforeseen risks can derail a project if not properly managed.
- Solution: Conduct thorough risk assessments, develop risk mitigation plans, and continuously monitor and manage risks throughout the project lifecycle.
- Stakeholder Management: Managing stakeholder expectations and ensuring their engagement can be challenging.
- Solution: Identify all stakeholders early in the project, understand their needs and expectations, and maintain regular communication to keep them informed and involved.
- Technological Disruptions: Rapid technological changes can impact project execution and outcomes.
- Solution: Stay updated with the latest technological trends, invest in training for the project team, and be flexible in adapting to new technologies.
Project management challenges are inevitable, but with proactive planning and effective strategies, they can be managed successfully. By addressing issues such as scope creep, communication breakdowns, resource management, and risk management, project managers can enhance project performance and achieve their goals.
FINAL 4 TIPS FOR ASPIRING PROJECT MANAGERS
- Get Certified: Certifications like the PMI’s Project Management Professional (PMP) can enhance credibility and provide valuable skills.
- Learn from Experience: Each project provides lessons. Reflect on what went well and what can be improved.
- Build Soft Skills: Skills like leadership, management, negotiation, empathy, and adaptability are essential for dealing with diverse teams and challenges.
- Embrace Continuous Learning: The field of project management is constantly evolving. Stay updated with new trends, methodologies, and tools.
